Medilink West Midlands has announced Entec Health as a shortlisted candidate for Partnership with NHS, in its Medical and Healthcare Business Awards 2015. The Awards event will take place at Malmaison Birmingham on 14 January 2016 and is set to start the year with a great flourish for the ventures which will be celebrated for their expertise, commitment and success.
"I am delighted that Entec Health's collaboration with the NHS to support best practice in wound care for the benefit of patients has been recognised by the panel", said Achala Patel, Founder and Managing Director of Entec Health.
Over the past 4 years, Entec Health has developed strong engagement with a wide range of NHS Trusts to explore a new evidence-based approach in wound management practice, enabled by digital technology.
Currently there is unacceptable variability in the standard of chronic wound care practice and outcomes achieved across the NHS nationally (1). Wound Care provision for patients with chronic wounds has a high cost to the NHS, estimated at £3billion per annum. (2,3).
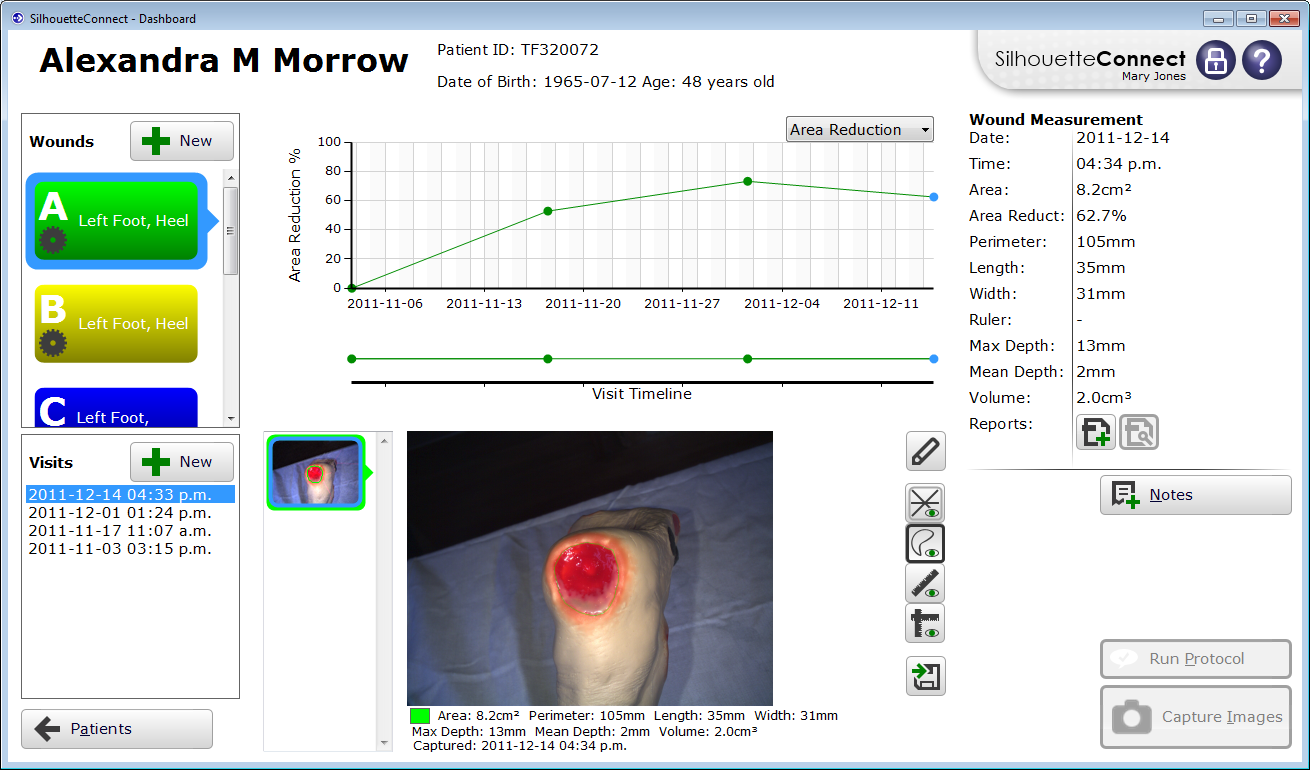
Entec Health has an active NHS partnering programme which involves informing and engaging NHS stakeholders on the advantages of adopting digital wound assessment and wound informatics to address this “clinical excellence and cost-effectiveness gap” in wound management. The Silhouette system (ARANZ Medical) helps clinicians to capture, document and share digital wound images and objective, quantified wound healing data across a care pathway to support improved clinical practice, patient experience and service transformation.
Entec Health is collaborating with innovator clinical champions and NHS Trusts to embed Silhouette as an enabler technology for evidence-based care and open up opportunities to improve the cost-effectiveness and efficiency of managing patients with chronic and acute wounds.
The Partnership with NHS Award category is sponsored by West Midlands AHSN. You can find further details via the link.
http://www.medilinkwm.co.uk/events/medilinkwm-medical-and-healthcare-business-awards-2015
Book a Silhouette demonstration and discussion meeting with Entec Health:
Download the Silhouette Prospectus to learn more:
Download Electronic Data Capture for Wound Care paper:
Download Silhouette King's Diabetes Foot Care Case Study:
References:
- The need for EU standards in wound care: an Irish survey. Moore Z, Cowan S. (2005).
- Wounds UK, 1(1): 20-8.The Smith and Nephew Foundation: Skin Breakdown – The Silent Epidemic. Posnett J, Franks P.J. (2007). The cost of skin breakdown and ulceration in the UK. Smith and Nephew Foundation, Hull.
- The resource costs of wound care in Bradford and Airedale primary care trust in the UK. Vowden K, Vowden P, Posnett J. (2009). Journal of Wound Care; 18: 93- 102.
- The use of electronic data capture devices in wound care settings. J.Fletcher, Wounds UK 2012, Vol 8, No 4
- Going Digital, case study of early adopter experience with Silhouette, Kings College Hospital NHS Foundation Trust, Diabetic Foot Clinic, London, UK. M.Bates, March 2013, Online Case Study Publication, NHS High Impact Innovations Showcase.